Use the admin panel
Administrators have access to the admin panel, where useful information about the platform can be found, such as the users, the bots running and done, and more. From the admin panel, you can also update packages installed on the platform and restart the platform.
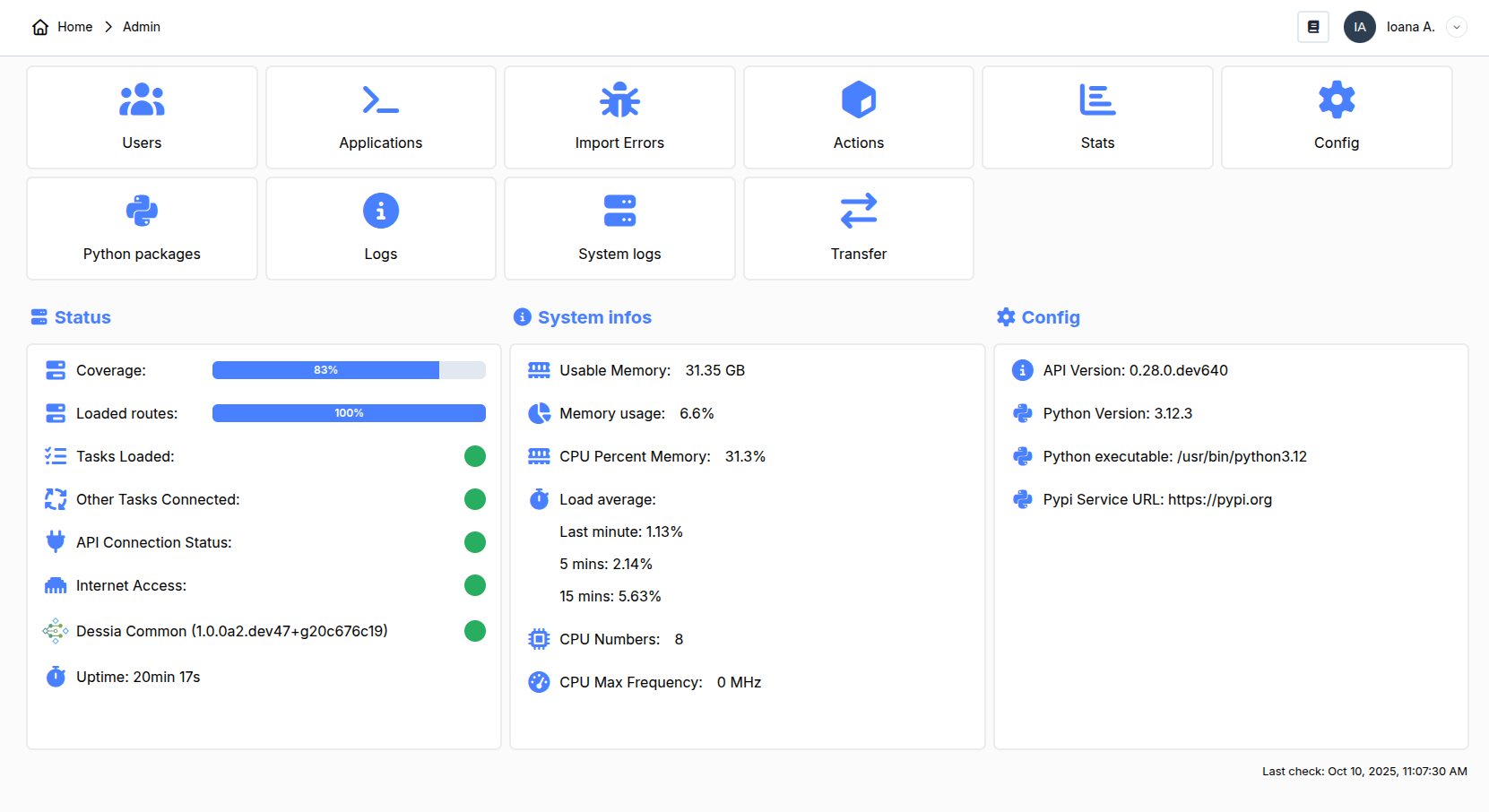
All sections will be covered but attention will be drawn to the most useful sections.
1. Users
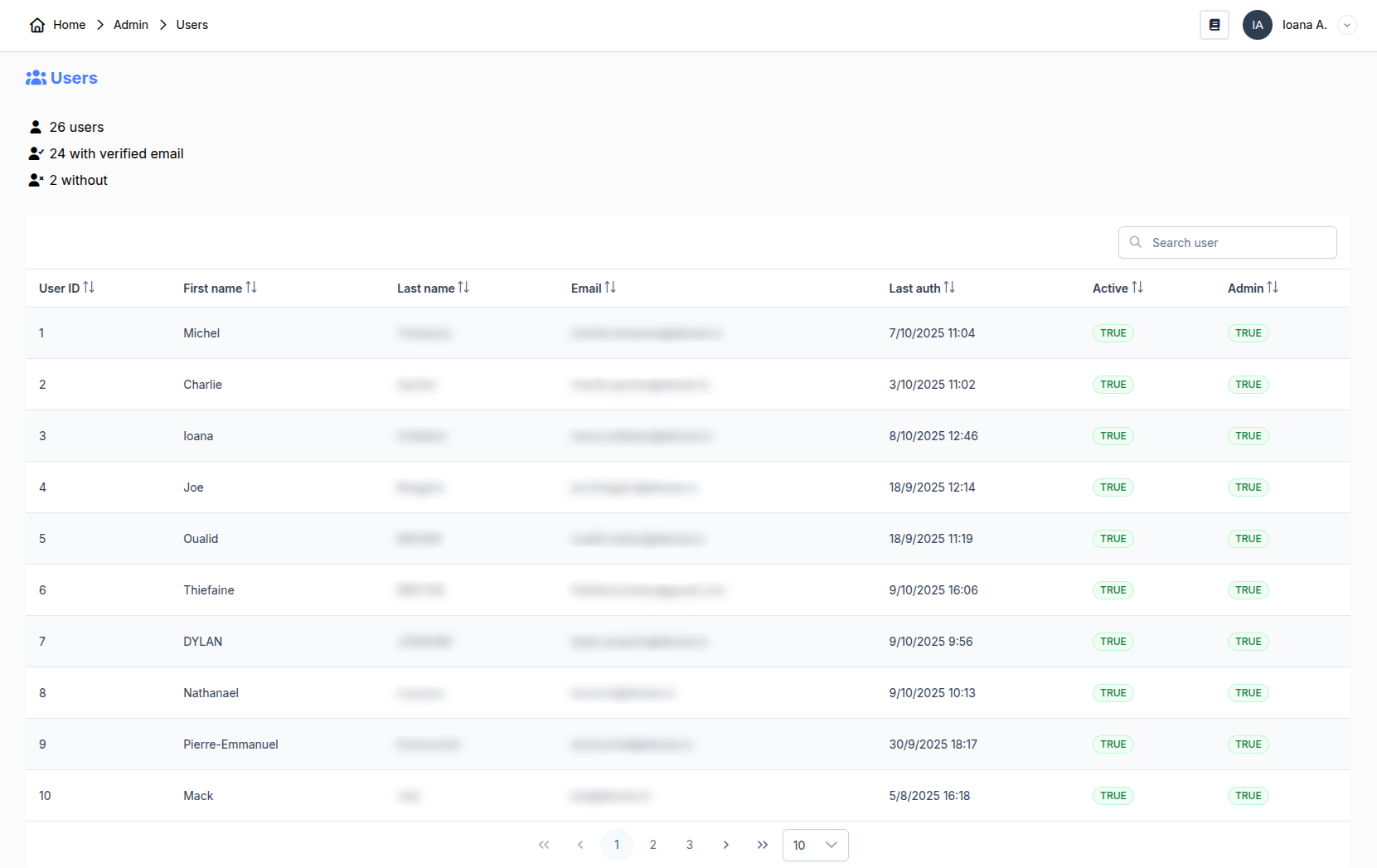
In this section, all accounts created on the platform are registered. From there, you have access to their name, email address, organization (if they have one), the last time they logged in, and if their account is active or admin.
By clicking on a user, you have access to additional actions such as activating their account or granting them administrator rights. We will dive deeper into this in the next chapter called Activate Accounts and Assign Administrators. From this popup menu, you can also reset a user's password by selecting Generate Reset Password Link and sending them the obtained link.
2. Packages
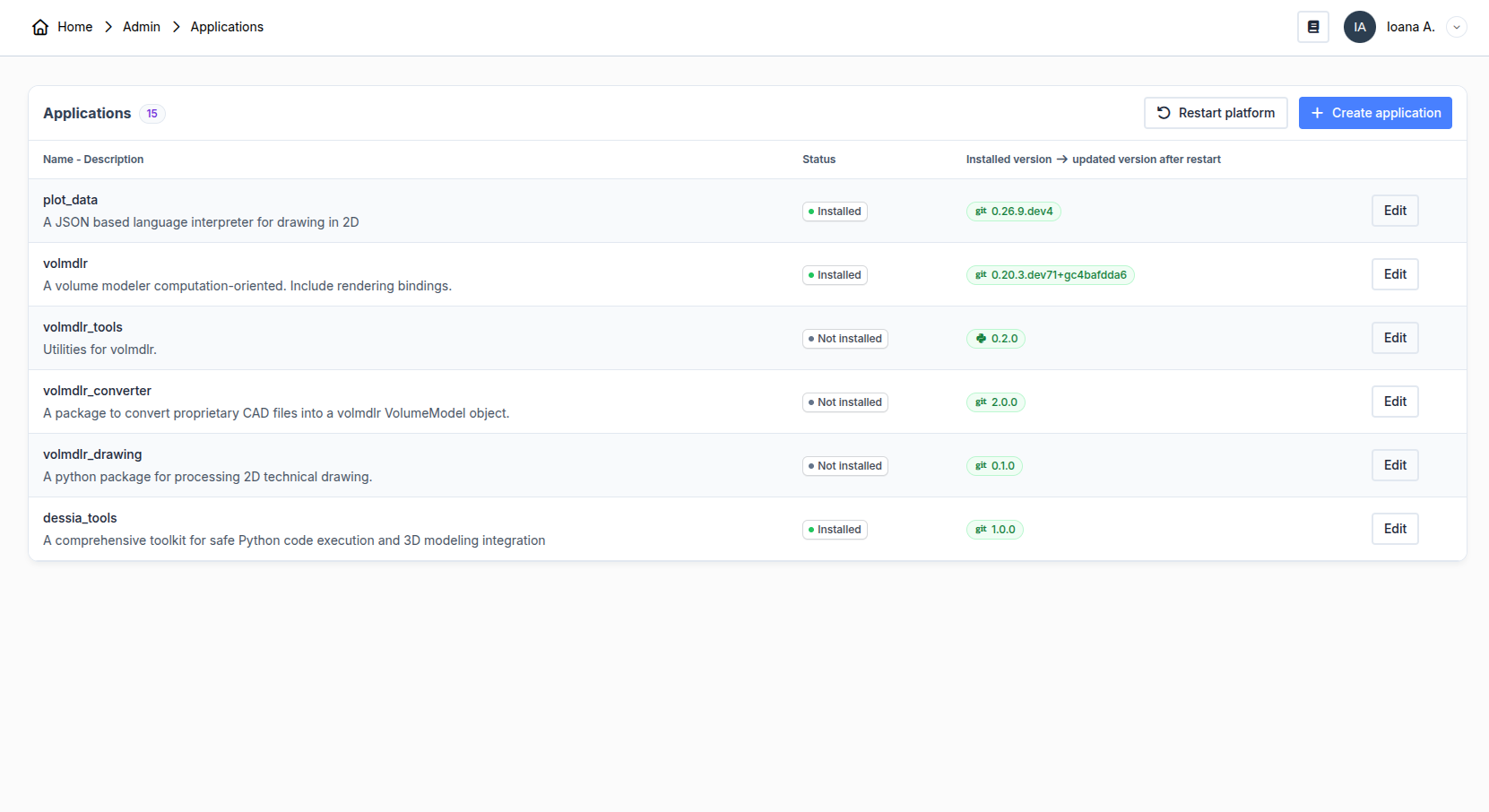
Managing packages is an important part of the life of a platform. You can install and update packages that have already been installed by clicking the CREATE APP button.
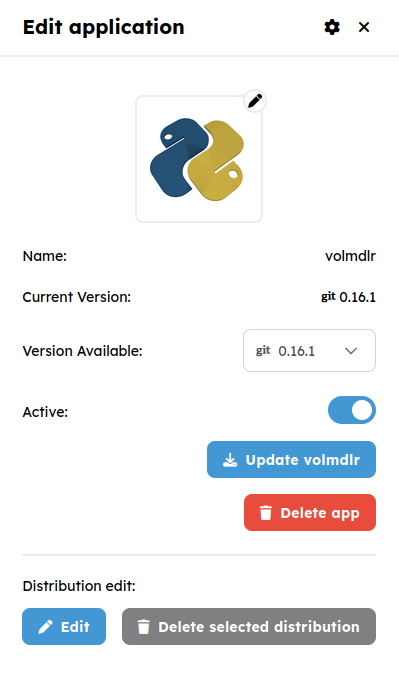
If you select a package, you will be able to change its version, enable, disable, update or delete it. Moreover, packages created using a Git distribution, the Edit button will be available to manually switch commits on a given Git branch.
More details about packages can be found in the chapters Manage packages and Install the required packages
3. Import Errors
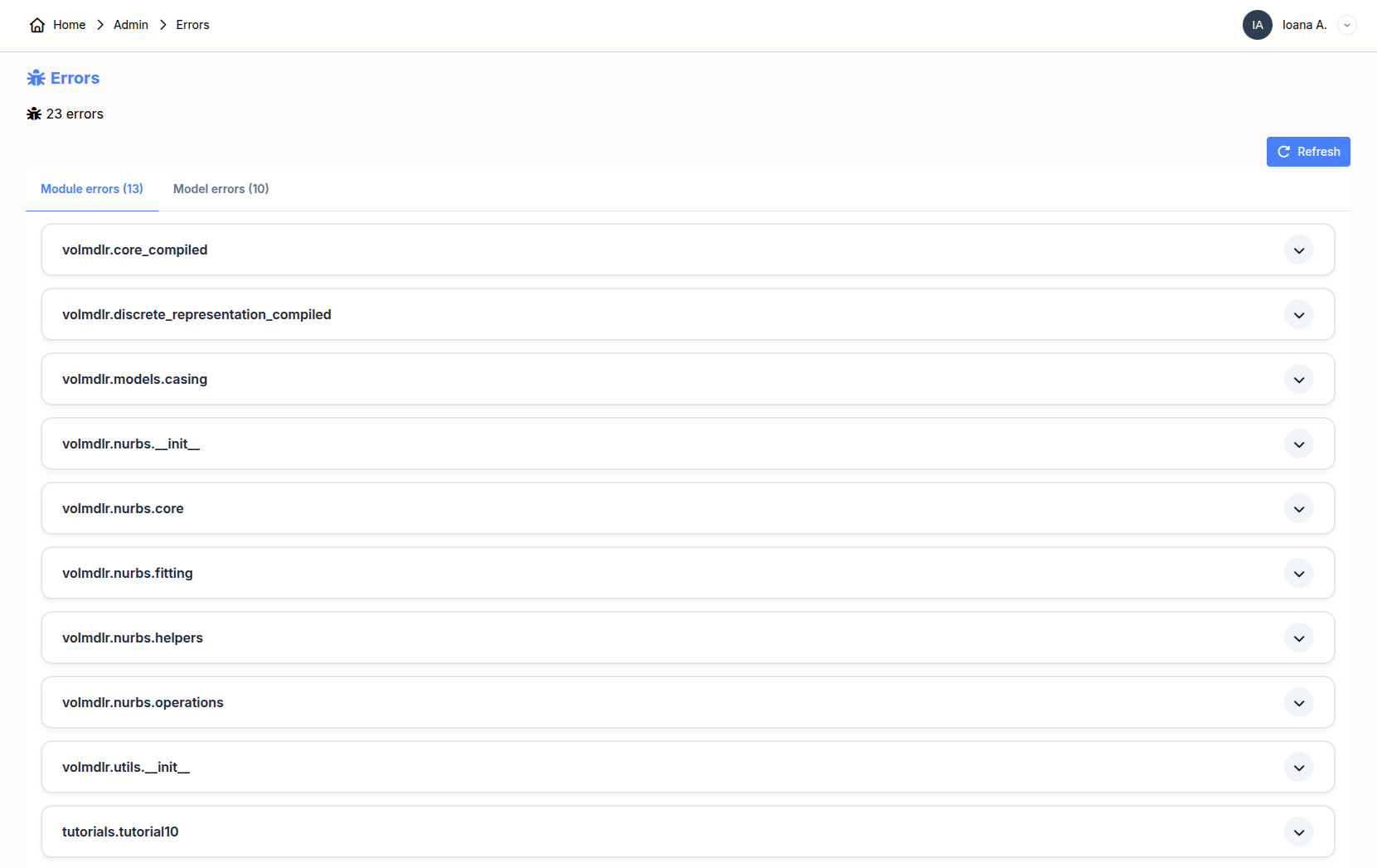
This section warns you about errors encountered when installing packages. Ideally, you don't want any errors. However, if you have some, as long as it doesn't concern models you work with, it won't impact your experience on the platform. If it deals with a model you are using or a whole package, you can click the error to get additional information.
4. Actions
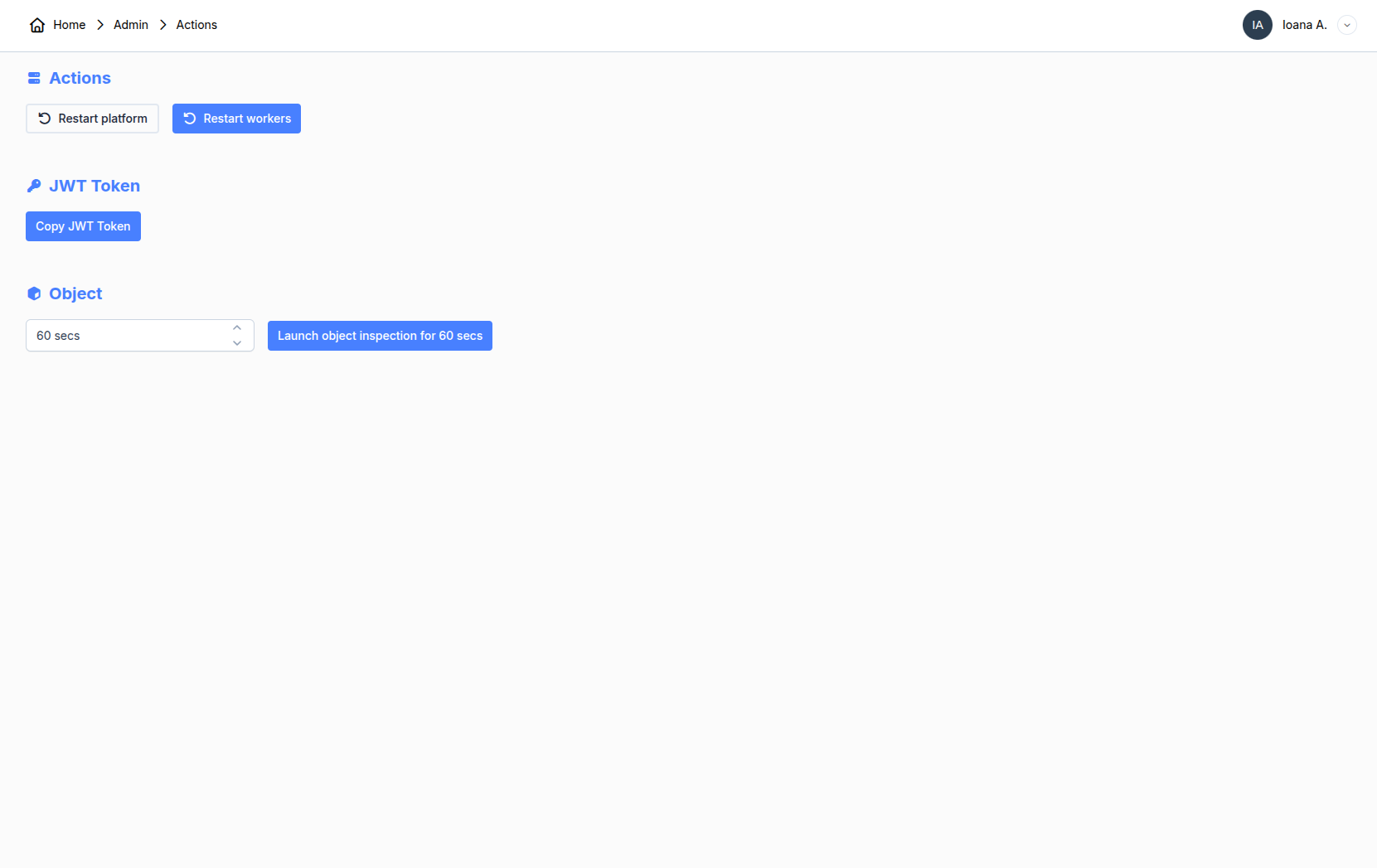
As an administrator, you can perform different actions on the platform. The main action consists of restarting the platform. It is necessary when new versions of packages are installed. You can also restart the workers if you have unexplained troubles with running your bots.
The other functionalities are more advanced and won't be discussed here.
5. Stats
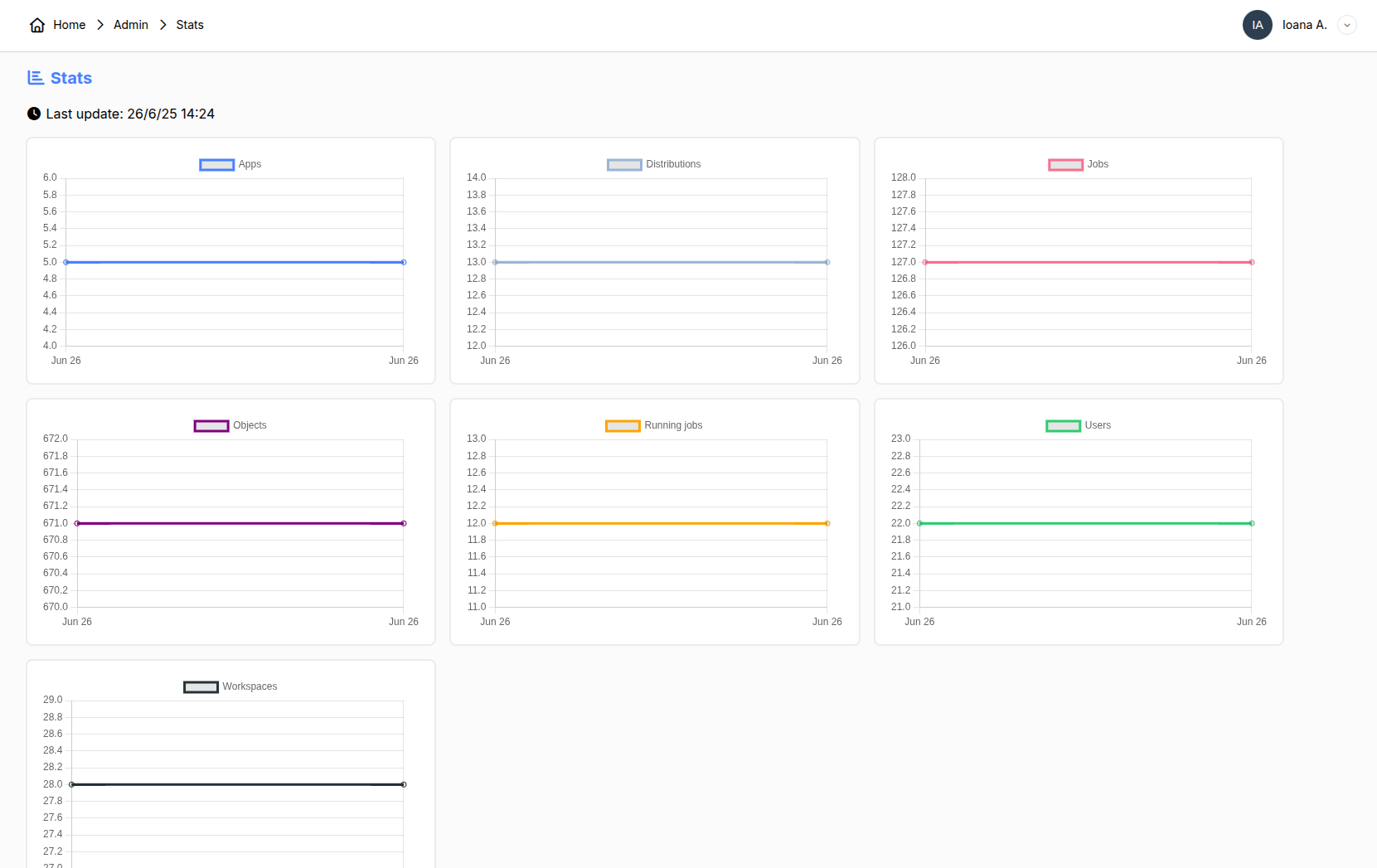
The stats provide insights over time about the platform, such as the number of users, the quantity of objects in the database, and more.
6. Config
This section contains additional technical information about the platform, the license manager section and platform settings to manage low-code features. For the license manage see License System Section.
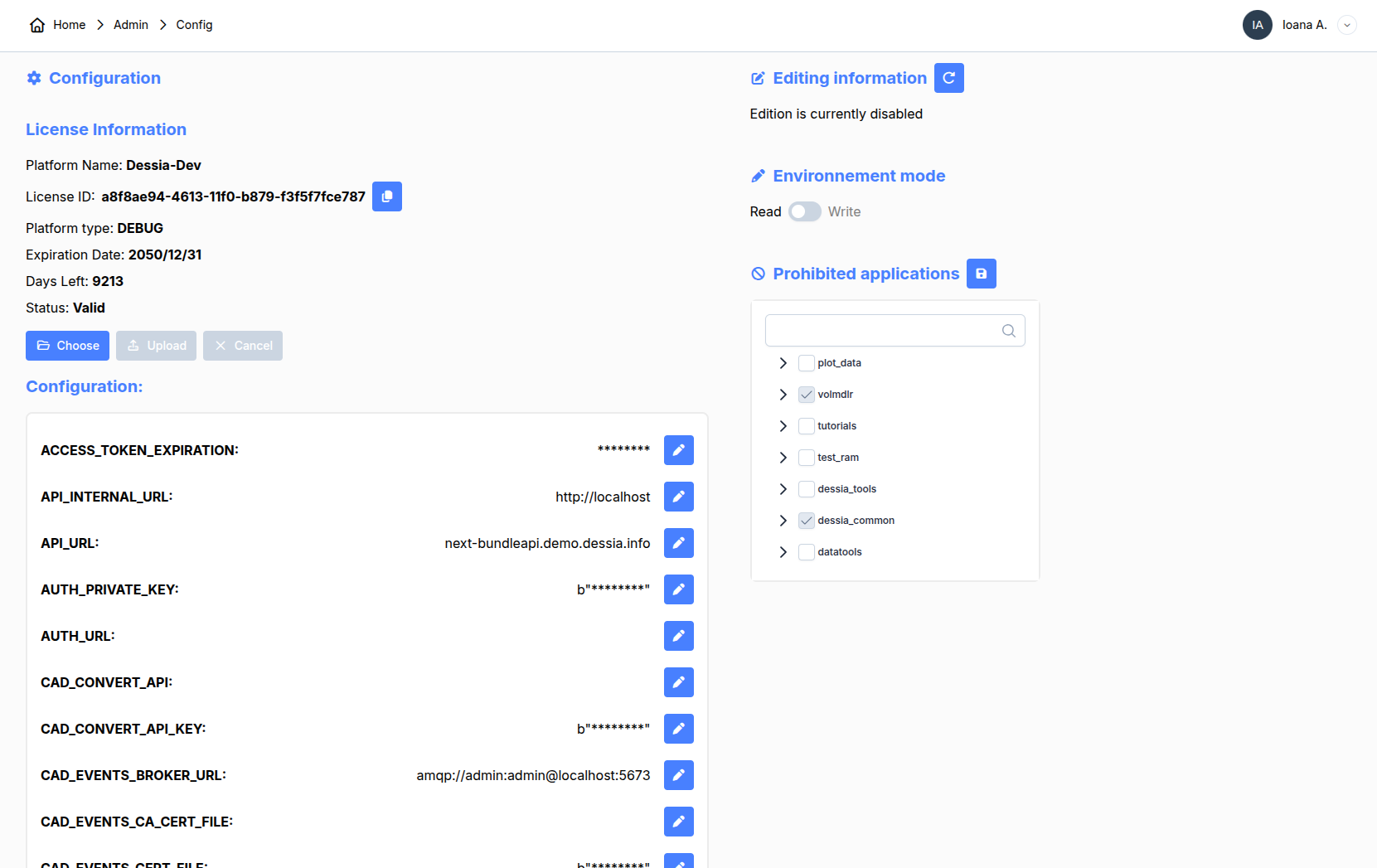
Prohibited package
This tree shows all modules that are in your packages. When you install a package and you restart the platform, new ones will appears here.
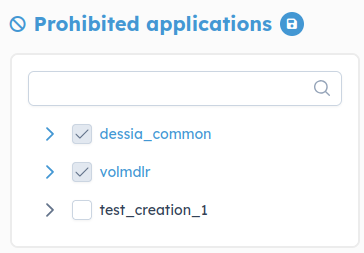
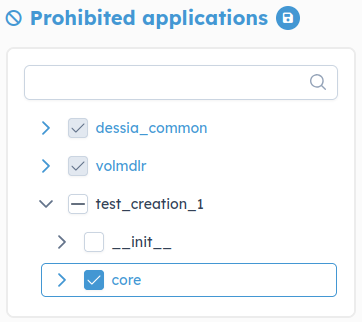
You can select modules that you don't want to be modified and then save. hat will allow you to control which part of the package is frozen.
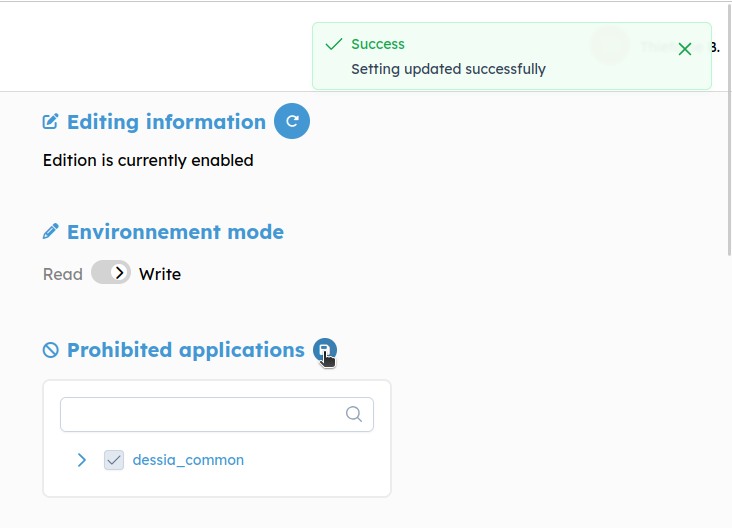
After saving you'll be notified that changes are take into account
You'll see prohibited package on Low-code navigation with a little lock besides their name
![]()
Environment mode
If you don't want at all to give access to Low-Code modification features (ex: If your on a prod instance) you can block all modification request by setting to read mode, witch is the default state of the platform.
Editing Information
Modification feature need to be single edition. The Editing Information section say if there is someone who modify one package. For now this constrain is actualize when the user make a save, is not active until 30 minute or force by pressing the reset button
![]()

Say that the user First Last is editing
After refreshing, the edition is now possible for the first to reach Low-code section
7. Python packages
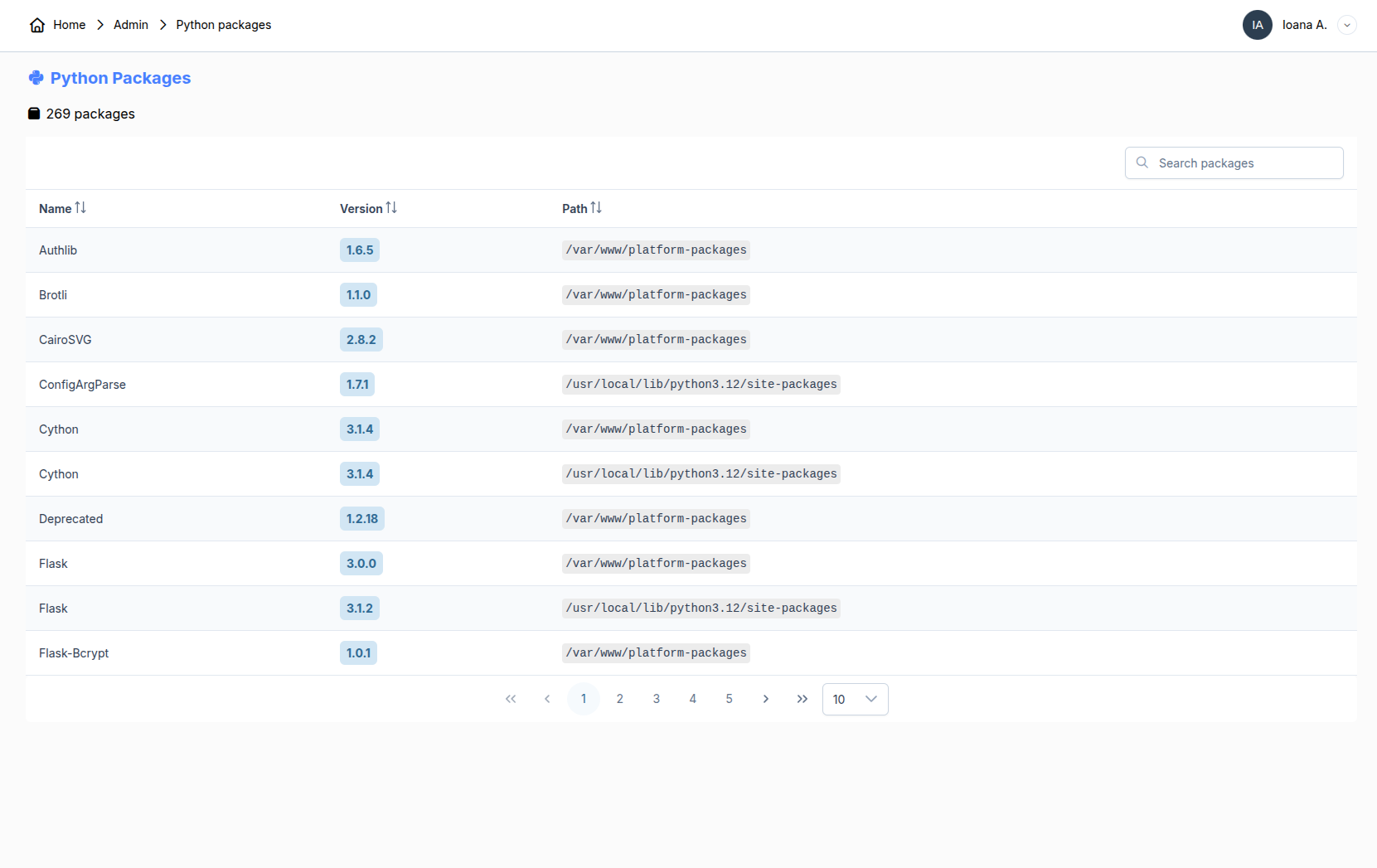
All the installed packages can be found in this table. You can search for specific ones using the search bar. You can check the installed version as well as the path.
8. Logs
From here, you can see two different logs. First, the logs of the platform giving insights on errors, details about the actions made on the platform, such as resetting a password, restarting the workers, and other technical information.. The second tab shows the authentication logs, i.e. who logged in to the platform and at what time.
9. System logs
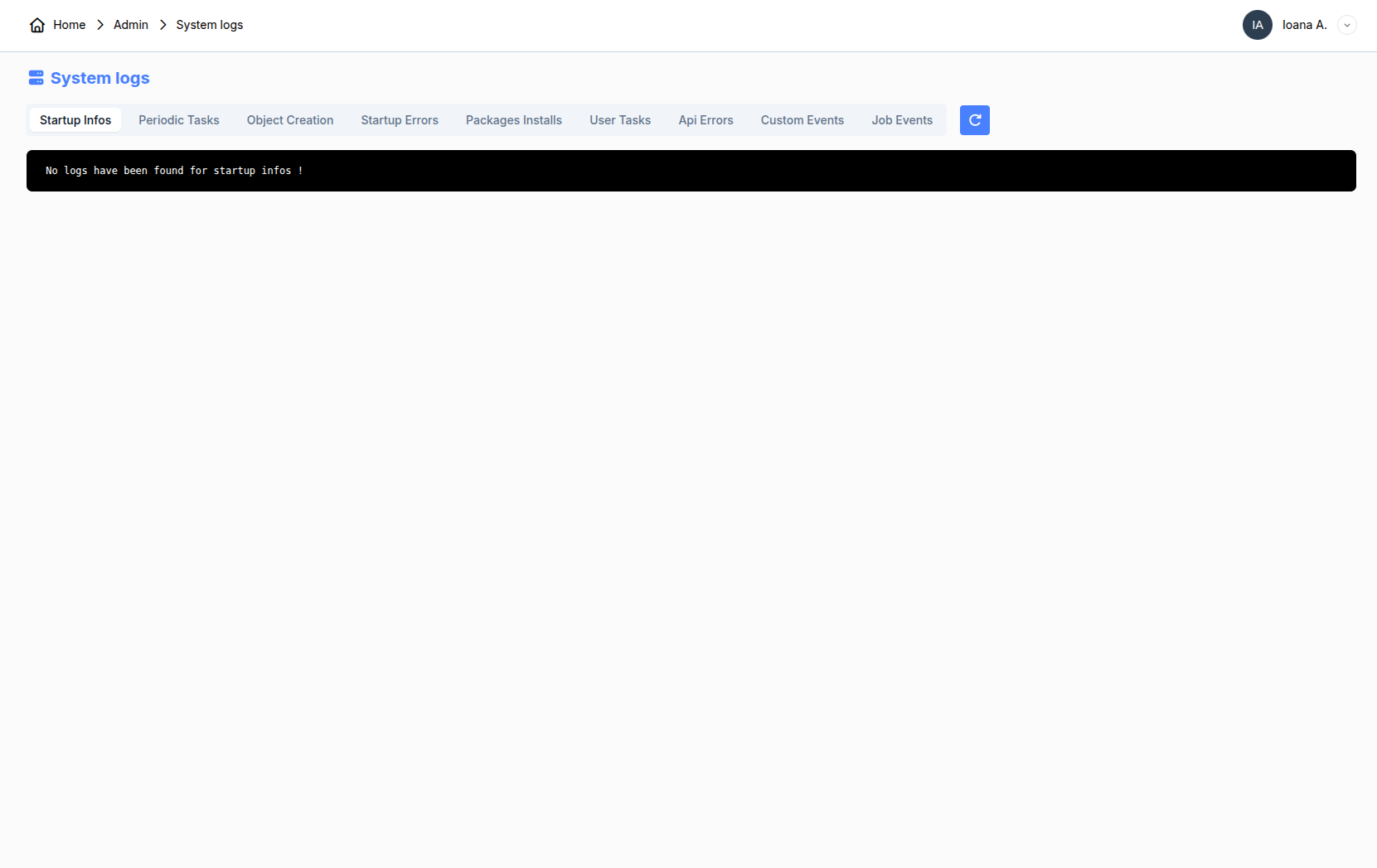
The system logs are useful for understanding if something went wrong on the platform. You will find 6 different tabs: startup info, periodic tasks, startup errors, packages installs, user tasks, api errors.
10. Transfer
Packages can be transferred from a platform to another one. For this you will need the url of the platform with the package you want to install, and a token. A JWT token, or JSON Web Token, is a compact and self-contained method for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. Get your token from the Action section in the admin panel.