Pattern Matching#
Pattern matching enables finding occurrences of reference shapes within larger assemblies using graph-based subgraph isomorphism.
Note
Prerequisites: Attributed Adjacency Graph (AAG), GraphAssembly
Pattern Matcher Module#
The Pattern Matcher module provides tools for finding geometric patterns within assembly structures. It uses graph-based subgraph isomorphism to identify occurrences of a reference shape (pattern) within a larger assembly.
Overview#
Pattern matching is essential for:
Component identification: Find all instances of a specific part (screws, bolts, bearings)
Quality assurance: Verify that required components are present in assemblies
Design analysis: Identify repeating structural elements
Cost estimation: Count occurrences of specific parts
The module combines two key technologies:
Attributed Adjacency Graphs (AAG) for geometric representation
VF2 subgraph isomorphism algorithm for pattern matching
Class: PatternMatcher#
Description#
The PatternMatcher class searches for specific subgraph patterns within a GraphAssembly structure, focusing on solid geometries and their face relationships.
Constructor#
from volmdlr_tools.features import PatternMatcher
matcher = PatternMatcher(
graph_assembly: GraphAssembly,
angular_tol: float = 1e-6,
min_similarity: float = 1.0,
min_face_signature_similarity: float = 1.0,
name: str = ""
)
Parameters:
graph_assembly: The assembly graph to search withinangular_tol: Angular tolerance in radians for edge matchingmin_similarity: Minimum similarity threshold (1.0 = exact match)min_face_signature_similarity: Minimum face signature similarityname: Instance name
Methods#
find_pattern_matches(pattern_graph) -> list[Match]#
Find all occurrences of a pattern graph within the assembly.
matches = matcher.find_pattern_matches(pattern_graph=aag_pattern)
Parameters:
pattern_graph: AnAttributedAdjacencyGraphrepresenting the pattern to search for
Returns:
List of
Matchobjects, each containing the faces that match the pattern
find_matches_from_multiple_patterns(patterns) -> list[list[int]]#
Search for multiple different patterns in a single pass.
all_matches = matcher.find_matches_from_multiple_patterns(patterns=[pattern1, pattern2])
Class: Match#
A match result containing the matched faces and their bounding geometry.
Attributes#
Attribute |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The matched face objects |
|
|
Shell created from matched faces |
|
|
Oriented bounding box enclosing the match |
|
|
Coordinate frame of the bounding box |
|
Color for visualization |
Methods#
# Get visualization primitives
primitives = match.volmdlr_primitives()
Matching Modes#
Exact Matching (default)#
When min_similarity=1.0, the matcher uses exact subgraph isomorphism:
Node matching: Target node degree >= pattern node degree
Edge matching: Angles must match within
angular_tolFace signatures must match within
min_face_signature_similarity
matcher = PatternMatcher(
graph_assembly=assembly_graph,
min_similarity=1.0, # Exact matching
angular_tol=1e-6
)
Approximate Matching#
For finding similar but not identical patterns:
matcher = PatternMatcher(
graph_assembly=assembly_graph,
min_similarity=0.8, # Allow 80% similarity
min_face_signature_similarity=0.9
)
Approximate matching considers:
Node count similarity
Surface area similarity
Bounding box volume ratios
Complete Example#
from volmdlr_tools.features import PatternMatcher
from volmdlr_tools.graph.faces import AttributedAdjacencyGraph
from volmdlr_tools.graph.assembly import GraphAssembly
import volmdlr
from volmdlr import model, shapes
# Load assembly and pattern
folder = "data/step/"
volume_model = model.VolumeModel.from_step(folder + "HAWT Gear Assembly.STEP")
pattern_model = model.VolumeModel.from_step(folder + "hex-screw-pattern1.step")
# Create AAG for the pattern
aag_pattern = AttributedAdjacencyGraph(pattern_model.primitives[0])
# Create graph assembly and pattern matcher
graph_assembly = GraphAssembly.from_volume_model(volume_model)
pattern_matcher = PatternMatcher(graph_assembly=graph_assembly)
# Find all matches
matches = pattern_matcher.find_pattern_matches(pattern_graph=aag_pattern)
print(f"Found {len(matches)} pattern matches")
# Visualize results
prims = []
for match in matches:
color = volmdlr.utils.common_operations.random_color()
match.color = color
prims.extend(match.volmdlr_primitives())
model.VolumeModel([volume_model, *prims]).babylonjs()
Visual Examples#
Pattern to Search#
The reference pattern (hex screw):
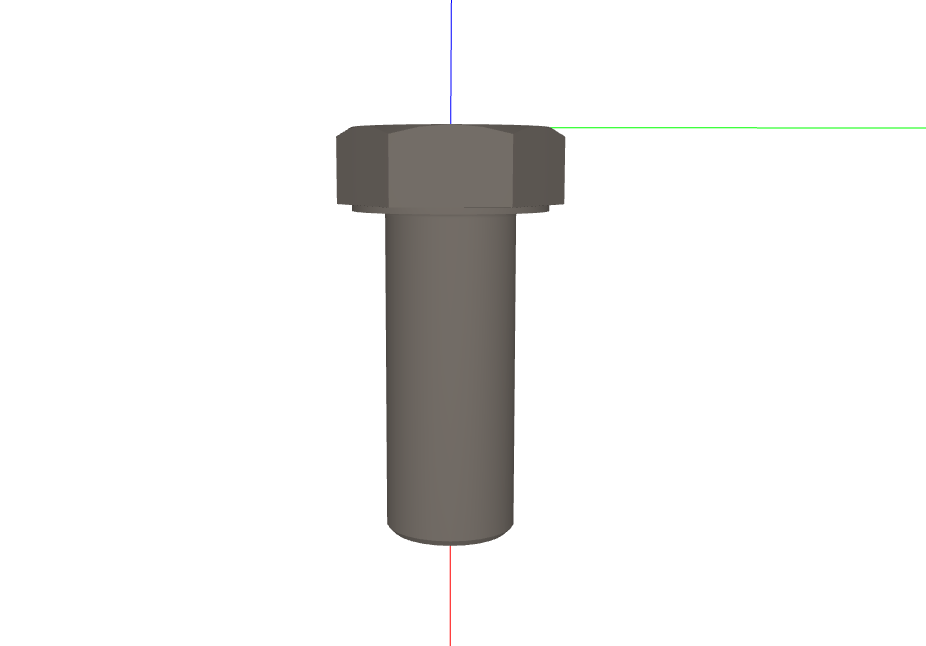
Assembly to Search Within#
The gearbox assembly:
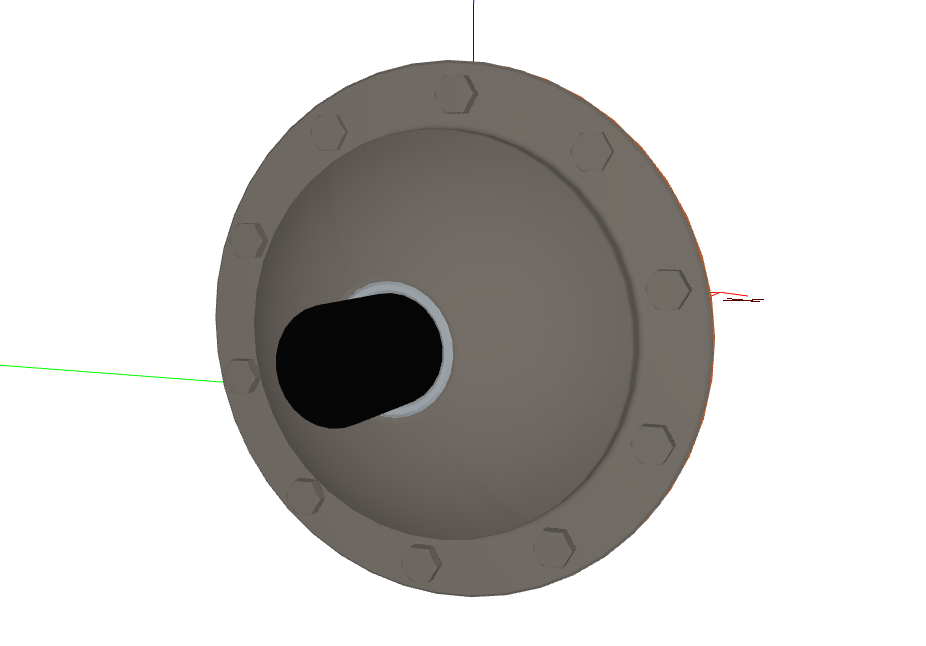
Found Patterns#
All identified hex screws highlighted:
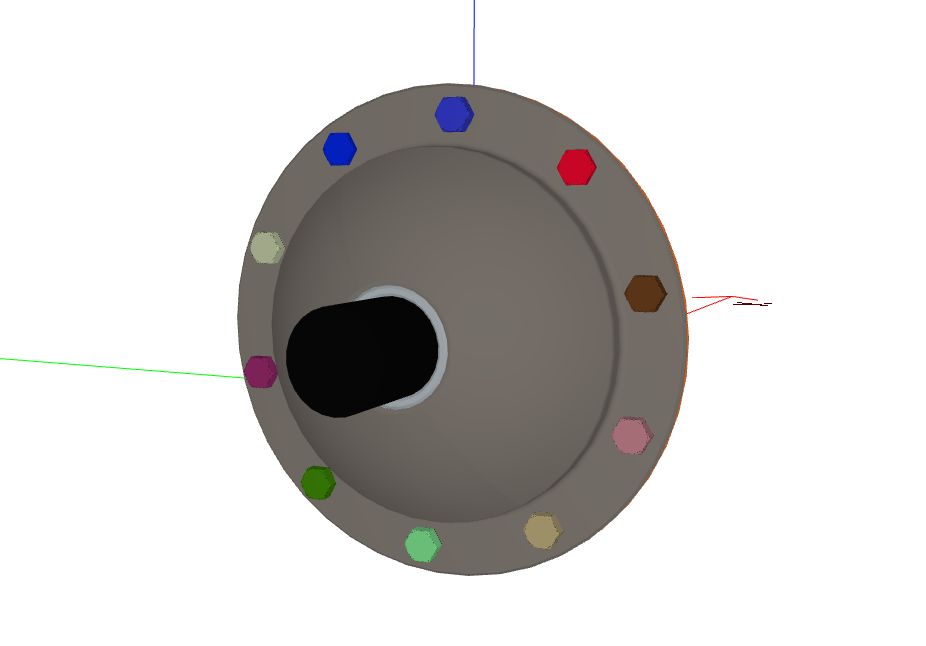
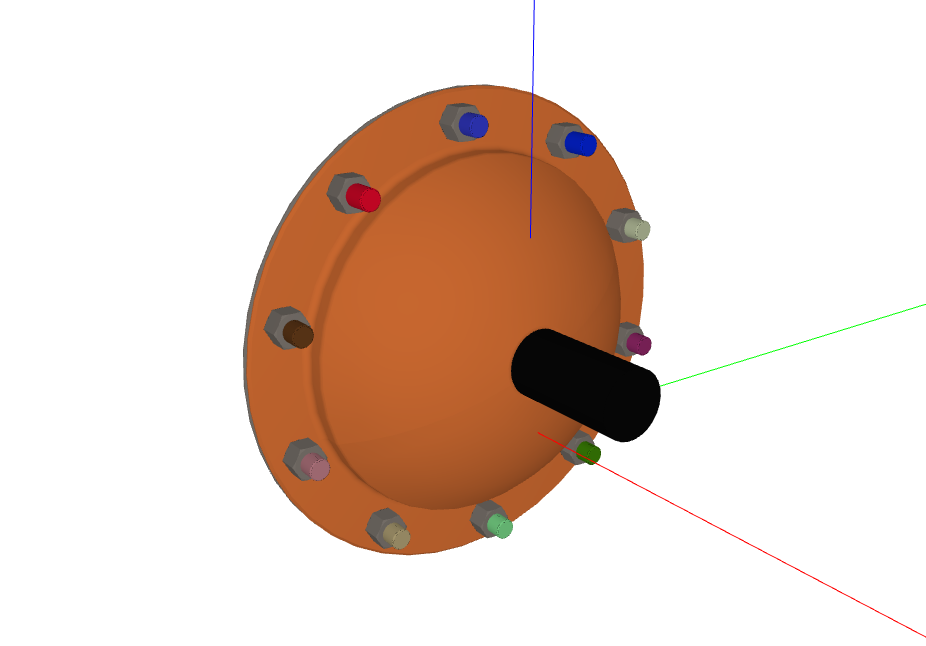
How It Works#
1. Pattern Preparation#
Before matching, the pattern graph is prepared:
from volmdlr_tools.features.pattern_matcher import prepare_graph
prepare_graph(pattern_graph, tolerance=1.0, n_bins=150, n_points=10000)
This calculates:
Face angles between adjacent faces
Node degrees in the graph
Face-related attributes (signatures, areas)
2. Graph Traversal#
The matcher iterates through all Shell nodes in the assembly:
for solid_node in graph_assembly.get_nodes(
lambda node: graph_assembly[node]["class"] == "Shell"
):
aag = graph_assembly.get_aag(solid_node)
# ... perform matching
3. Subgraph Isomorphism#
The VF2 algorithm finds subgraph mappings where:
Node attributes match (degree, face signatures)
Edge attributes match (angles between faces)
4. Overlap Prevention#
Matches are filtered to avoid overlapping:
Visited nodes are tracked
Only non-overlapping matches are returned
Performance Considerations#
Large assemblies: Pattern matching complexity grows with assembly size
Pattern size: Larger patterns reduce false positives but increase matching time
Tolerance: Tighter tolerances reduce false positives but may miss valid matches
Face signatures: Pre-computing signatures improves matching accuracy
Use Cases#
Finding Fasteners#
# Load fastener patterns
bolt_pattern = AttributedAdjacencyGraph(bolt_shape)
nut_pattern = AttributedAdjacencyGraph(nut_shape)
washer_pattern = AttributedAdjacencyGraph(washer_shape)
# Find all fasteners
all_matches = matcher.find_matches_from_multiple_patterns(
[bolt_pattern, nut_pattern, washer_pattern]
)
Quality Verification#
# Verify expected component count
matches = matcher.find_pattern_matches(critical_component_pattern)
expected_count = 8
if len(matches) != expected_count:
print(f"Warning: Expected {expected_count} components, found {len(matches)}")
Assembly BOM Generation#
# Build component count for Bill of Materials
component_patterns = {
"M6 Bolt": bolt_m6_pattern,
"M6 Nut": nut_m6_pattern,
"Bearing 6205": bearing_pattern,
}
bom = {}
for name, pattern in component_patterns.items():
matches = matcher.find_pattern_matches(pattern)
bom[name] = len(matches)
See Also#
Attributed Adjacency Graph (AAG) - Attributed Adjacency Graph fundamentals
GraphAssembly - Assembly graph representation
../shape_analysis/signature - Shape signatures for similarity matching