Attributed Adjacency Graph (AAG)#
The Attributed Adjacency Graph (AAG) is a graph representation of face adjacencies in a BRep (Boundary Representation) model. It is the foundation for all feature recognition operations.
Note
Prerequisites: Graph Fundamentals
Attributed Adjacency Graph (AAG) Module Documentation#
Overview#
The Attributed Adjacency Graph (AAG) module provides a graph-based representation of the adjacency relationships between faces in a BRep (Boundary Representation) model. It enhances the BRep model with additional attributes such as surface types, angles between faces, and geometric properties, facilitating graph-based traversal and feature recognition.
This module is based on the work of Joshi and Chang (1988) and S. E. Slyadneva and V. E. Turlapov(2020), which proposed a graph-based heuristic for recognizing machined features in 3D solid models.
The attributed adjacency graph is a graph where each node represents a face of a solid and the edges represent the connections between these faces. For each edge, we assign the type of connection between the faces.
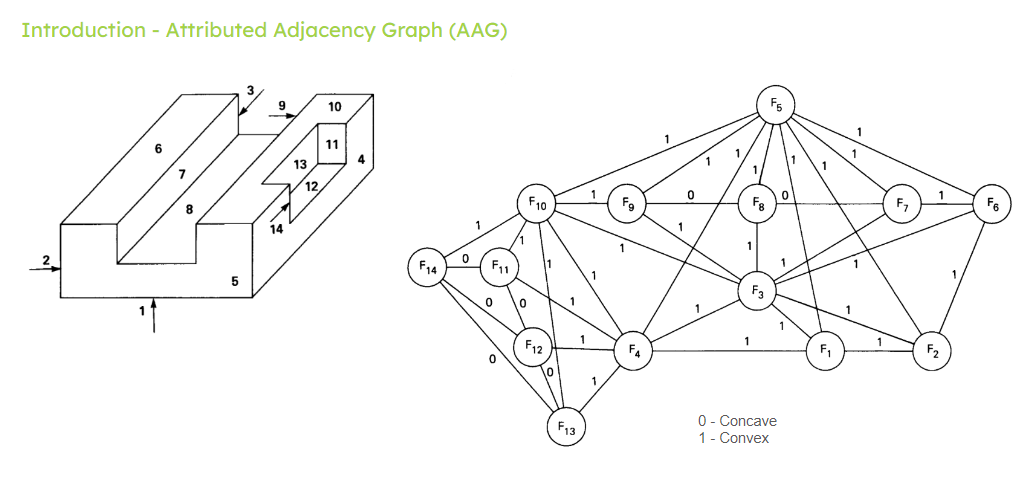
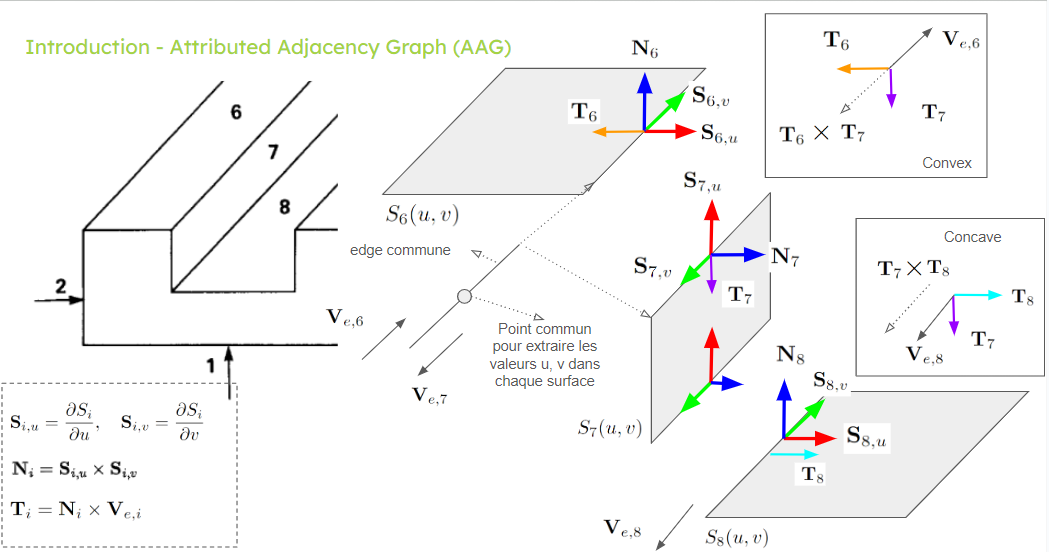
To determine the type of connection between the faces, we start by extracting the surface and the common edge between each pair of adjacent faces. Then, we choose a point on this common edge and use it to calculate the parameters of this point in each face. With this information, we calculate the derivatives in the (u) and (v) directions. Using the vector product of these derivatives, we can calculate the normal of each face, which we call (N) in the figure below.
The common edge has a certain orientation in each face. To represent this orientation, let’s suppose a vector (V), which is a tangent vector on the edge at the chosen point, indicating its direction and orientation on the face. We use this vector to calculate a vector (T = N x V).
The final step is to calculate the angle between the vector (T) of each pair of faces, using the vector (V) of the first face of the pair as a reference. If this angle is negative ((T_1 x T_2) has the opposite orientation to (V_1)), then we have a convex connection. If this angle is zero or positive, then we have a concave transition. See image below
Key Features#
Formal graph view of the CAD model for applying graph algorithms.
Caches serial indices of sub-shapes to avoid repeated use of TopExp utilities for unchanged CAD models.
Representation of features and semantics through graph attributes.
Efficiently defines adjacency relationships between faces, aiding feature recognition and geometric analysis.
Class: AttributedAdjacencyGraph#
Description#
The AttributedAdjacencyGraph class represents an adjacency graph of the faces in a BRep model. Each node in the graph represents a face, and edges capture the adjacency relationships between faces sharing common edges.
Constructor#
AttributedAdjacencyGraph(shape: Union[shapes.Solid, shapes.Shell],
graph: Optional[nx.Graph] = None,
allow_smooth: bool = True,
smooth_angular_tol: float = 1e-6,
name: str = "")
Parameters#
shape: (Union[shapes.Shell, shapes.Solid]): The BRep model shape.graph: (Optional) The networkx graph of the shape if already available.allow_smooth: (Optional) Flag to allow smooth edges between adjacent faces.smooth_angular_tol: (Optional) Tolerance for detecting smooth edges.name: (Optional) name for the graph.
Attributes#
selected_faces(TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape): Stores selected faces.child_parent_map(TopTools_IndexedDataMapOfShapeListOfShape): Stores relationships between edges and their parent faces.map_faces(TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape): Indexed map of faces.map_vertices(TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape): Indexed map of vertices.map_edges(TopTools_IndexedMapOfShape): Indexed map of edges.map_edges_faces(TopTools_IndexedDataMapOfShapeListOfShape): Map of edges to their adjacent faces.graph(nx.Graph): The adjacency graph storing nodes (faces) and edges with attributes.
Methods#
build_adjacency_graph() -> None#
Builds the adjacency graph by iterating over the edges of the BRep model, adding nodes and edges for adjacent faces.
add_mates(mate_faces: list[TopoDS_Shape]) -> None#
Adds adjacency relationships (mates) between pairs of adjacent faces. It computes the angle between them, assigns surface types and colors to nodes, and adds edges between faces in the graph.
Parameters#
mate_faces(list[TopoDS_Shape]): List of faces that share a common edge.
get_face(face_index: int) -> TopoDS_Shape#
Retrieves a face from the indexed map by its index.
Parameters#
face_index(int): The index of the face to retrieve.
Returns#
TopoDS_Shape: The face corresponding to the given index.
get_edge(edge_index: int) -> TopoDS_Shape#
Retrieves an edge from the indexed map by its index.
Parameters#
edge_index(int): The index of the edge to retrieve.
Returns#
TopoDS_Shape: The edge corresponding to the given index.
get_neighbors(face_index: int) -> list[int]#
Retrieves the neighboring faces of a given face based on adjacency relationships in the graph.
Parameters#
face_index(int): The index of the face to retrieve neighbors for.
Returns#
list[int]: A list of indices representing neighboring faces.
get_neighbors_thru(face_index: int, edge: TopoDS_Shape) -> list[int]#
Retrieves the neighboring faces of a given face that share a specific edge.
Parameters#
face_index(int): The index of the face to find neighbors for.edge(TopoDS_Shape): The edge shared by neighboring faces.
Returns#
list[int]: A list of indices representing neighboring faces that share the specified edge.
get_neighbors_thru_edge_ids(face_index: int, edge_ids: TColStd_PackedMapOfInteger) -> list[int]#
Retrieves neighboring faces of a given face that share common edges, identified by their edge indices.
Parameters#
face_index(int): The index of the face to find neighbors for.edge_ids(TColStd_PackedMapOfInteger): A packed map of edge indices to check for commonality.
Returns#
list[int]: A list of indices representing neighboring faces that share the specified edges.
plot_data(reference_path: str = "#", **kwargs) -> list#
Generates a plot_data object to visualize the graph using the attributes stored in the adjacency graph.
Parameters#
reference_path(str): The reference path for the plot. Defaults to"#".
Returns#
list: A list ofplot_graph.NetworkxGraphobjects representing the visualized graph.
See Also#
Graph Fundamentals - Base graph concepts
GraphAssembly - Assembly-level graphs
../shape_analysis/feature_recognition - Uses AAG for feature detection