Feature Processor#
The main entry point for extracting geometric features from BRep shapes.
Note
Prerequisites: Attributed Adjacency Graph (AAG)
Feature Recognition Module#
This module provides tools to recognize and extract various features from Boundary Representation (BRep) shapes, such as blends, cavities, sharp edges, and sheet metal features, through graph-based algorithms. It aims to simplify the process of analyzing complex 3D models.
Note: As of V0.6.0, the module has been restructured. The old class names (
FeaturesRecognizer,RecognizeBlends,RecognizeCavitivies) remain available as aliases for backward compatibility, but the new names are recommended for new code.
FeatureProcessor - The Main Entry Point#
The FeatureProcessor class is the main orchestrator for feature recognition and manipulation. It provides a clean API for:
Feature extraction: Blends, cavities, sharp edges, and sheet metal features
Feature querying: Count, existence checks, and type-specific access
Feature filtering: By radius, depth, category, location, and more
Visualization: Display features in a 3D viewer
Constructor#
from volmdlr_tools.features import FeatureProcessor
processor = FeatureProcessor(
shape: Union[shapes.Shell, shapes.Solid],
aag: Optional[AttributedAdjacencyGraph] = None,
name: str = ""
)
Parameters:
shape: The BRep shape to analyze (Shell or Solid)aag: (Optional) Pre-computed Attributed Adjacency Graphname: (Optional) Instance name
Feature Extraction Methods#
General Extraction#
Method |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Extract all available features (auto-detects sheet metal) |
|
Extract blend/fillet features |
|
Extract cavity features (holes, pockets) |
|
Extract sharp edge features |
Sheet Metal Specific Extraction#
Method |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Extract all sheet metal features (bends, jogs, notches, etc.) |
|
Extract deformation features (emboss, flanged cutouts) |
|
Extract lance features |
Usage Examples#
from volmdlr_tools.features import FeatureProcessor
from volmdlr.model import VolumeModel
# Load shape
volume_model = VolumeModel.from_step("part.step")
shape = volume_model.primitives[0]
# Create processor
processor = FeatureProcessor(shape=shape)
# Option 1: Extract all features automatically
processor.extract_all()
# Option 2: Extract specific features
processor.extract_blends(max_radius=0.05)
processor.extract_cavities()
processor.extract_sharp_edges()
# Option 3: For sheet metal parts
if processor.is_sheet_metal:
processor.extract_sheet_metal_features()
Feature Access Properties#
After extraction, access features through read-only properties that return immutable tuples:
General Features#
Property |
Returns |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
All extracted blend features |
|
|
Blends grouped by connectivity and radius |
|
|
All cavity features (includes Round, Rectangular, Slotted) |
|
|
All sharp edge features |
Sheet Metal Features#
Property |
Returns |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Sheet metal bend features |
|
|
Offset bend (jog) features |
|
|
Notch cut features |
|
|
Corner features |
|
|
Corner relief features |
|
|
Emboss deformation features |
|
|
Lance features |
|
|
Louvre features |
|
|
Unclassified features |
Usage Examples#
# Access blends
for blend in processor.blends:
print(f"Blend radius: {blend.blend_attribute.radius}")
# Access blend chains
for chain in processor.blend_chains:
print(f"Chain with {len(chain)} blends, radius: {chain.radius}")
# Access cavities
for cavity in processor.cavities:
print(f"Cavity type: {type(cavity).__name__}")
# Access sheet metal bends
for bend in processor.bends:
print(f"Bend angle: {bend.angle}")
Feature Query Methods#
get_feature_count() -> dict[str, int]#
Get count of all extracted features by type.
counts = processor.get_feature_count()
# {'Blend': 12, 'BlendChain': 4, 'Cavity': 3, ...}
for feature_type, count in counts.items():
print(f"{feature_type}: {count}")
has_features(feature_type=None) -> bool#
Check if features exist.
from volmdlr_tools.features.feature_types import Blend, Cavity
# Check if any features exist
if processor.has_features():
print("Features have been extracted")
# Check for specific feature type
if processor.has_features(Blend):
print(f"Found {len(processor.blends)} blends")
is_sheet_metal -> bool#
Check if the shape is recognized as sheet metal.
if processor.is_sheet_metal:
print("Shape is sheet metal - can extract bends, jogs, etc.")
processor.extract_sheet_metal_features()
else:
print("Standard part - extracting blends and cavities")
processor.extract_blends()
processor.extract_cavities()
Feature Filtering Methods#
Filter Blends#
filtered_blends = processor.filter_blends(
min_radius: float = None, # Minimum blend radius
max_radius: float = None, # Maximum blend radius
blend_type: str = None, # Blend type name
confirmed_only: bool = False # Only confirmed blends
)
Example:
# Get small fillets only
small_fillets = processor.filter_blends(max_radius=0.01)
# Get large fillets
large_fillets = processor.filter_blends(min_radius=0.05)
# Get fillets in a range
medium_fillets = processor.filter_blends(min_radius=0.01, max_radius=0.05)
Filter Blend Chains#
filtered_chains = processor.filter_blend_chains(
min_radius: float = None, # Minimum chain radius
max_radius: float = None, # Maximum chain radius
min_length: float = None, # Minimum chain length
max_length: float = None # Maximum chain length
)
Example:
# Get long blend chains
long_chains = processor.filter_blend_chains(min_length=0.1)
Filter Cavities#
filtered_cavities = processor.filter_cavities(
min_depth: float = None, # Minimum cavity depth
max_depth: float = None # Maximum cavity depth
)
Filter by Category (Sheet Metal)#
Filter features by their category:
# Get all cut features (slots, notches, corner reliefs)
cut_features = processor.filter_by_category("cut")
# Get all forming features (bends, jogs)
forming_features = processor.filter_by_category("forming")
# Filter by location too
boundary_cuts = processor.filter_by_category("cut", location="boundary")
internal_forming = processor.filter_by_category("forming", location="internal")
Valid categories: "cut", "forming", "blend", "cavity", "unknown"
Filter by Location (Sheet Metal)#
Filter features by their location on the sheet metal part:
# Get features on the boundary (perimeter)
boundary_features = processor.filter_by_location("boundary")
# Get internal features (holes, internal cutouts)
internal_features = processor.filter_by_location("internal")
Convenience Methods#
# Get all cut features
cuts = processor.get_cut_features(location=None) # or "boundary" / "internal"
# Get all forming features
forming = processor.get_forming_features(location=None)
Feature Management Methods#
Clear Features#
from volmdlr_tools.features.feature_types import Blend
# Clear all features
processor.clear_features()
# Clear specific feature type
processor.clear_features(feature_type=Blend)
# Clear and re-extract with different parameters
processor.clear_features()
processor.extract_blends(max_radius=0.1) # Different radius
Visualization#
show_features(feature_type=None)#
Display features in a 3D BabylonJS viewer.
from volmdlr_tools.features.feature_types import Blend, BlendChain, Cavity
# Show all features (extracts if needed)
processor.show_features()
# Show specific feature type
processor.show_features(feature_type=Blend)
processor.show_features(feature_type=BlendChain)
processor.show_features(feature_type=Cavity)
Each feature type is colored randomly for distinction.
Complete Workflow Example#
from pathlib import Path
from volmdlr.model import VolumeModel
from volmdlr_tools.features import FeatureProcessor
from volmdlr_tools.features.feature_types import Blend, BlendChain, Cavity
# Load the model
step_file = Path("data/step/nist_ctc_02_asme1_nx1980_rc-ap242e3.stp")
volume_model = VolumeModel.from_step(str(step_file))
shape = volume_model.primitives[0]
# Create processor
processor = FeatureProcessor(shape=shape)
# Check what kind of part this is
if processor.is_sheet_metal:
print("Processing sheet metal part...")
processor.extract_sheet_metal_features()
# Access sheet metal features
print(f"Bends: {len(processor.bends)}")
print(f"Jogs: {len(processor.jogs)}")
print(f"Notches: {len(processor.notches)}")
# Filter by location
boundary = processor.filter_by_location("boundary")
internal = processor.filter_by_location("internal")
print(f"Boundary features: {len(boundary)}")
print(f"Internal features: {len(internal)}")
else:
print("Processing standard part...")
processor.extract_all()
# Get feature counts
counts = processor.get_feature_count()
for name, count in counts.items():
print(f" {name}: {count}")
# Filter blends by radius
small_blends = processor.filter_blends(max_radius=0.01)
print(f"Small fillets (r<0.01): {len(small_blends)}")
# Access blend chains
for chain in processor.blend_chains:
print(f"Blend chain: radius={chain.radius:.4f}, length={chain.length:.4f}")
# Visualize all features
processor.show_features()
# Or visualize specific types
processor.show_features(feature_type=Blend)
Low-Level Extractors#
While FeatureProcessor is the recommended way to work with features, you can also use the lower-level extractor classes directly for more control.
BlendExtractor#
Identifies blend features (fillets/rounds) in a BRep model.
Attributes:
aag: The attributed adjacency graphmax_radius: Maximum allowable radiusids: List of face indices identified as blends
Methods:
perform(): Execute blend recognitionget_chains(): Get blend chains (grouped by connectivity and radius)get_blending_faces(): Get faces participating in blendsget_blending_chains_faces(): Get faces grouped by chain
CavityExtractor#
Detects cavities (pockets, holes) in a BRep model.
Methods:
get_pockets_faces(): Returns faces representing detected cavities
Visual Examples#
Blend Recognition#
from pathlib import Path
from volmdlr.model import VolumeModel
from volmdlr_tools.features import FeatureProcessor
from volmdlr_tools.features.feature_types import Blend, BlendChain, Cavity
# Load shape
step_file = Path("data/step/nist_ctc_02_asme1_nx1980_rc-ap242e3.stp")
volume_model = VolumeModel.from_step(str(step_file))
shape = volume_model.primitives[0]
# Create processor and extract blends
processor = FeatureProcessor(shape=shape)
processor.extract_blends(max_radius=0.05)
# Show blends
processor.show_features(feature_type=Blend)
Result:#
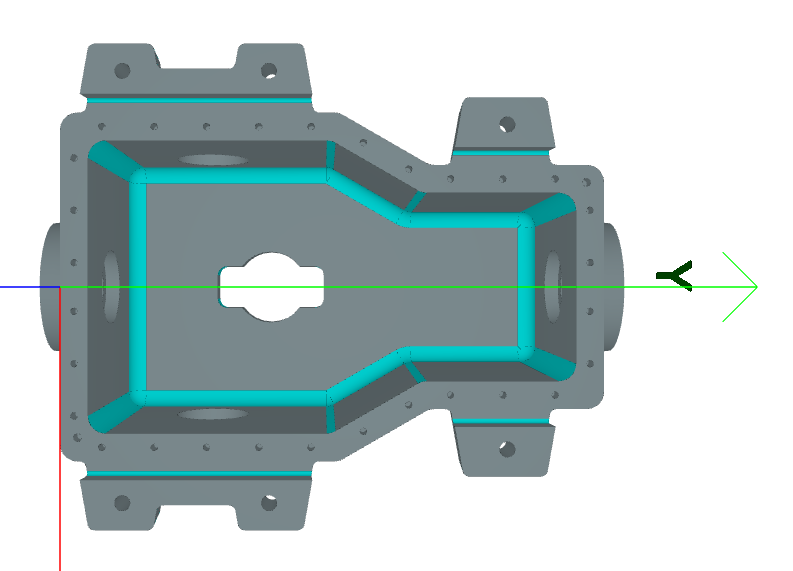
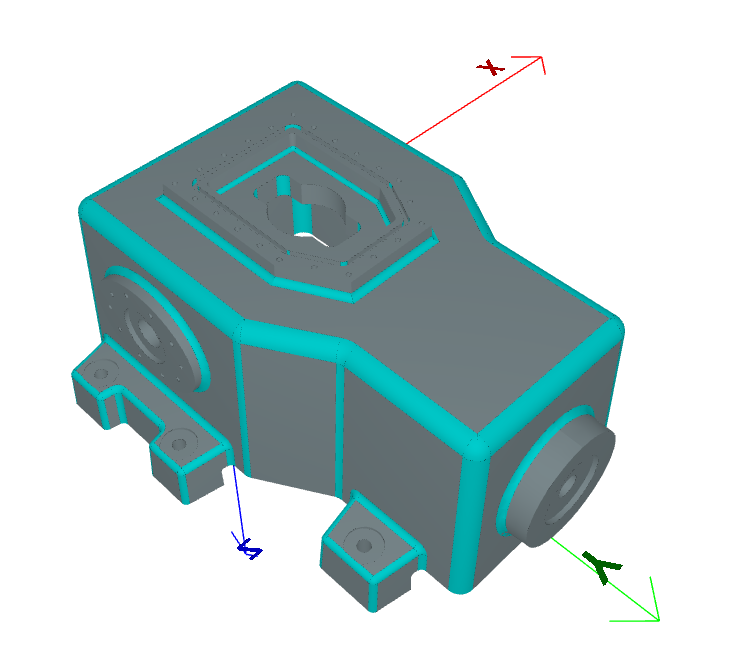
Blend Chains#
# Access blend chains (grouped by connectivity and radius)
for chain in processor.blend_chains:
print(f"Chain radius: {chain.radius}, length: {chain.length}")
# Visualize blend chains
processor.show_features(feature_type=BlendChain)
Result:#
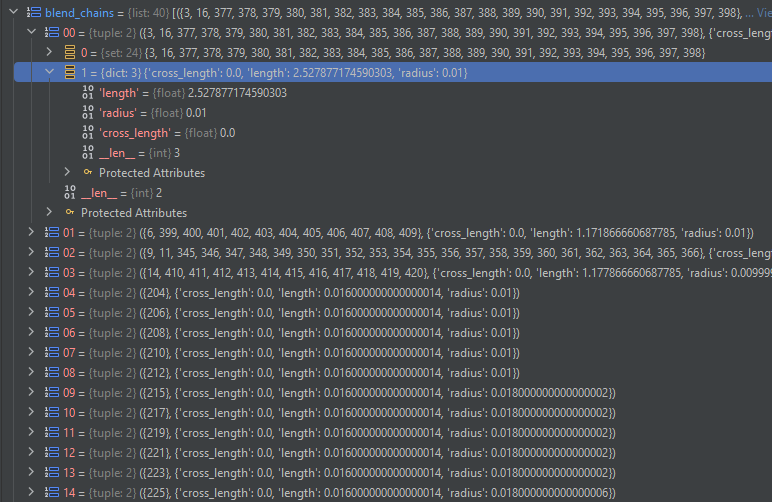
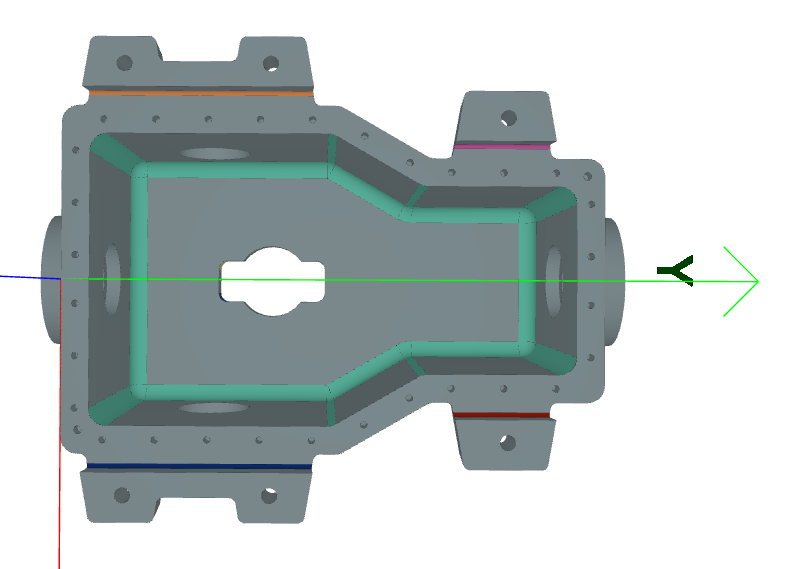
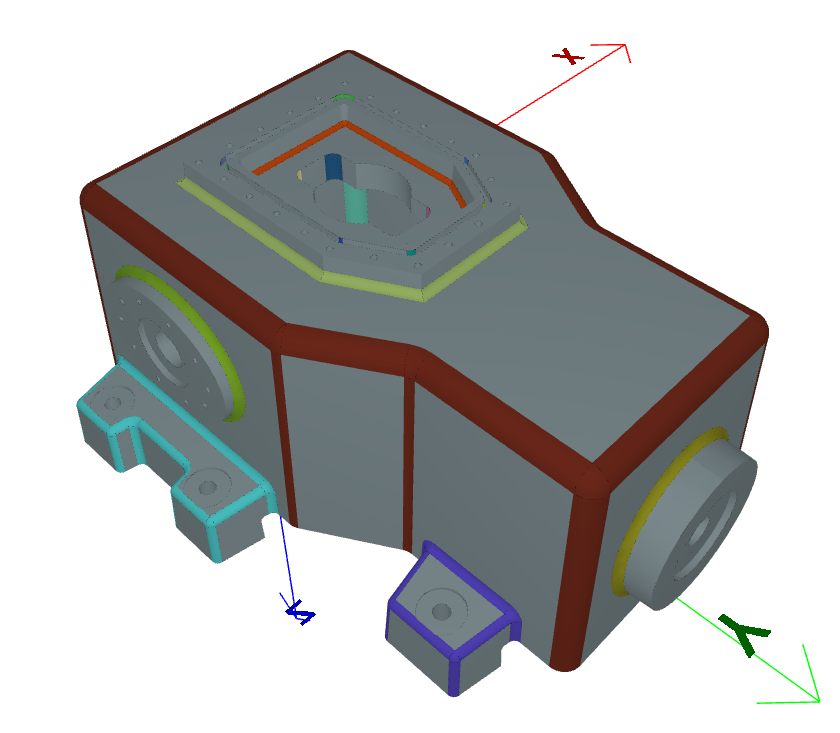
Cavity Recognition#
# Extract and visualize cavities
processor.extract_cavities()
# Access cavities
for cavity in processor.cavities:
print(f"Cavity type: {type(cavity).__name__}")
# Visualize
processor.show_features(feature_type=Cavity)
Result:#
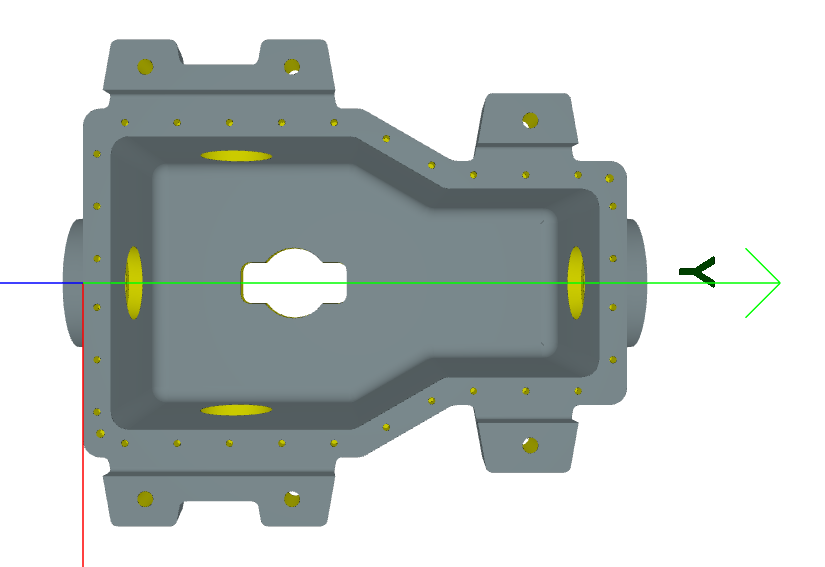
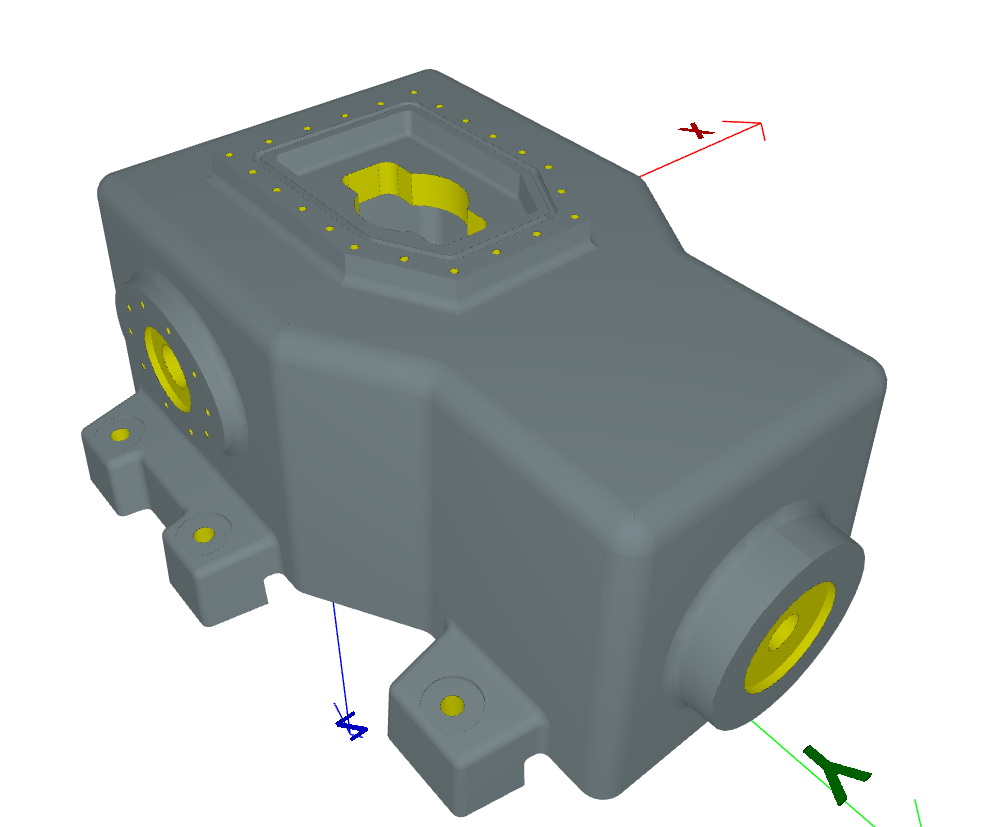
See Also#
Attributed Adjacency Graph (AAG) - Attributed Adjacency Graph
Sheet Metal Features - Sheet metal feature extraction
Sheet Metal Shapes - Sheet metal recognition