Useful operations#
Export to json file#
You can export any volmdlr objects to a json file. To do so, you can just call the method save_export_to_file.
Here is an example how you can save a plan face 3d to a .json file:
import volmdlr
from volmdlr import surfaces, faces
face = faces.PlaneFace3D.from_surface_rectangular_cut(surfaces.Plane3D(volmdlr.OXYZ), -1, 1, -1, 1)
face.save_export_to_file("json", 'path/to/where/to/save/your/file.json')
Import from json file#
If you have a json file containing volmdlr objects, you can use the method dessia_common.core.DessiaObect.from_json to import it.
Example:
import dessia_common
volmdlr_object = dessia_common.core.DessiaObject.from_json('path/to/your/file.json')
Matplotlib plots#
To have a matplotlib visualization of a volmdlr object in 2D or 3D, you can call the plot method in any object. See the following example
import volmdlr
from volmdlr import edges
from volmdlr.core import EdgeStyle
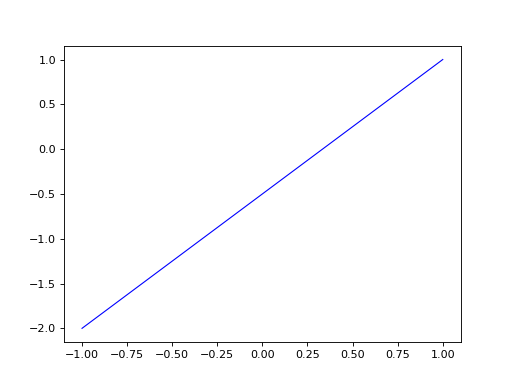
line_segment2d = edges.LineSegment2D(volmdlr.Point2D(1, 1), volmdlr.Point2D(-1, -2))
line_segment2d.plot(edge_style=EdgeStyle('b'))
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
Model Visualization#
To have a 3D visulaization of your model, most of the 3d objects has a babylonjs() method, which you can use to do so. Babylon.js is an open-source, JavaScript framework and engine for creating and rendering 3D graphics and games in web browsers. Here is an example on how you can do it.
from volmdlr import shapes
box = shapes.Solid.make_box(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
box.display_3d()