BOOLEAN OPERATIONS#
Boolean operations allow you to combine, subtract, or intersect solid
geometries. The shapes.Solid class provides the modern API for these
operations.
Creating primitive solids#
import math
import volmdlr
from volmdlr import shapes
# Create a box centered at origin
box = shapes.Solid.make_box(
length=0.2,
width=0.2,
height=0.2,
frame=volmdlr.Frame3D.oxyz(),
frame_centered=True,
name="box",
)
# Create a cylinder passing through the box
cylinder_frame = volmdlr.Frame3D(
origin=volmdlr.Point3D(-0.15, 0, 0),
u=volmdlr.Y3D,
v=volmdlr.Z3D,
w=volmdlr.X3D,
)
cylinder = shapes.Solid.make_cylinder(
radius=0.05,
height=0.3,
frame=cylinder_frame,
name="cylinder",
)
# Display both solids
volmdlr.model.VolumeModel([box, cylinder]).display_3d()
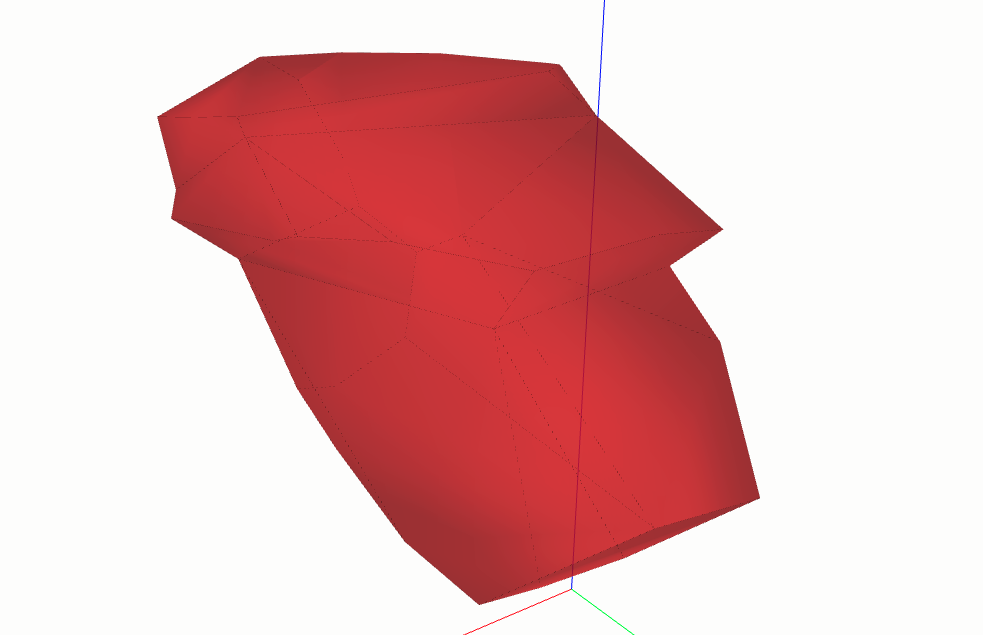
Union#
The union method combines two or more solids into a single shape.
union_solid = box.union(cylinder)
union_solid.display_3d()
If the solids do not intersect, the result is a compound containing both shapes. If one solid is completely inside another, the outer solid is returned.
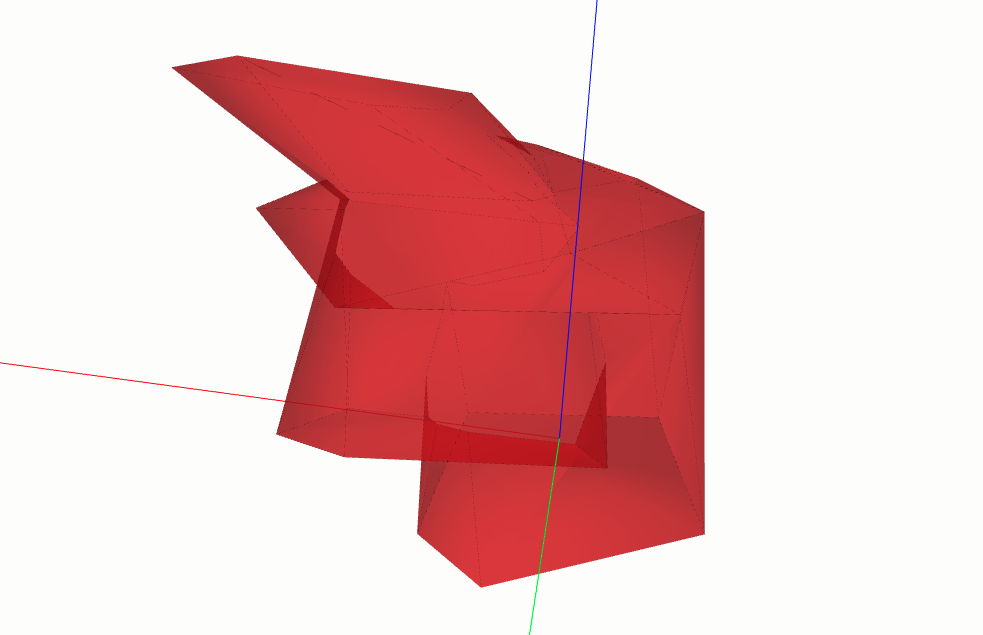
Subtraction#
The subtraction method removes material from the first solid where
it overlaps with the second.
subtracted = box.subtraction(cylinder)
subtracted.display_3d()
This creates a box with a cylindrical hole through it. Multiple solids can be subtracted in a single call.
# Subtract multiple cylinders at once
cylinder2 = cylinder.rotation(volmdlr.O3D, volmdlr.Z3D, math.pi / 2)
result = box.subtraction(cylinder, cylinder2)
result.display_3d()
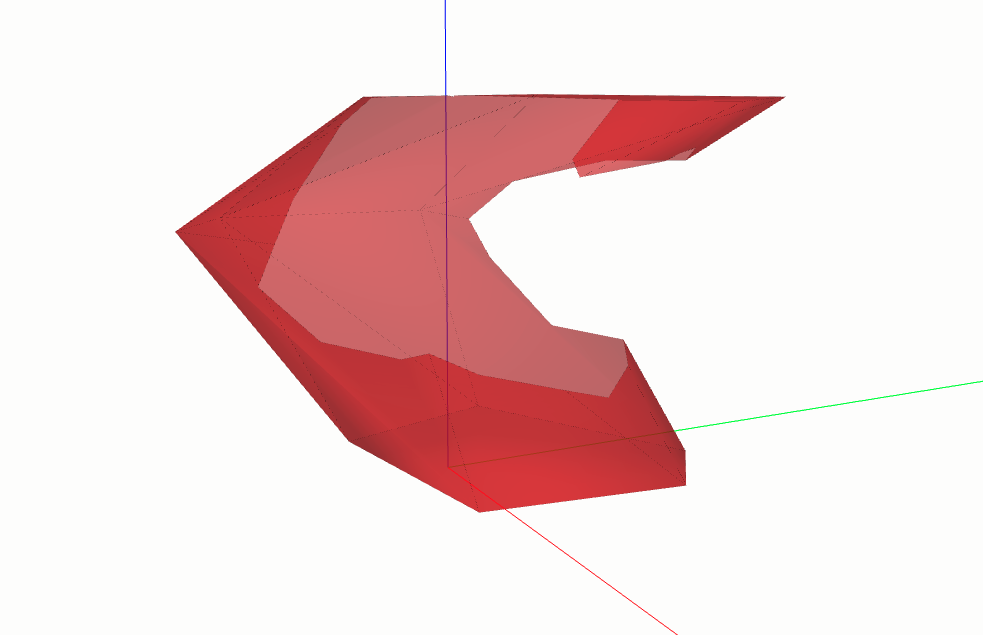
Intersection#
The intersection method returns only the volume where all solids
overlap.
intersection_solid = box.intersection(cylinder)
intersection_solid.display_3d()
This returns a cylinder segment with the length limited to the box dimensions.
Complete example#
Here is a complete example demonstrating all boolean operations:
import math
import volmdlr
from volmdlr import shapes
# Create a sphere
sphere = shapes.Solid.make_sphere(radius=0.1, name="sphere")
# Create a box centered at origin
box = shapes.Solid.make_box(
length=0.15,
width=0.15,
height=0.15,
frame_centered=True,
name="box",
)
# Union: combine both shapes
union_result = sphere.union(box)
print(f"Union volume: {union_result.volume():.6f}")
# Subtraction: remove box from sphere
subtraction_result = sphere.subtraction(box)
print(f"Subtraction volume: {subtraction_result.volume():.6f}")
# Intersection: keep only overlapping region
intersection_result = sphere.intersection(box)
print(f"Intersection volume: {intersection_result.volume():.6f}")
# Display results
union_result.display_3d()